4. Site Manager
The Site Manager allows FileZilla client users to store information about their FTP sites.
4.1 Starting Site Manager
The Site Manager command is located under the File menu. You can also press Ctrl+S or Command+S.
4.2 Site Manager Dialog
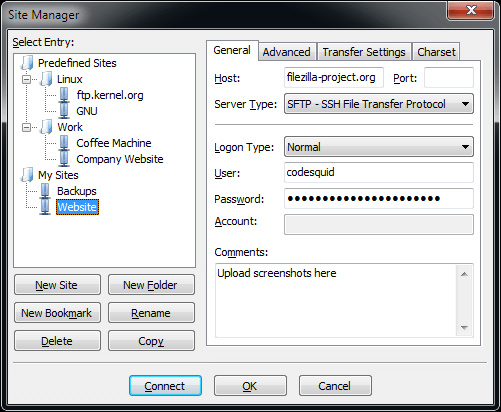
Use the Select Entry panel on the left to select the target site. Once a site is selected, you may do the following with it:
- Connect to
- Edit
- Copy
- Rename
- Delete
Use the New Folder button to introduce or add folders.
In the right panel, you have 4 tabs to enter some needed, and much optional, information about the selected site on the left.
4.2.1 General tab
- Host: Example: ftp.example.com
- Port: Only if it differs from the standards.
- Protocol: Enter the type of FTP server you will connect to (such as FTP or SFTP).
- Encryption: Whether, and how, the FTP connection should be encrypted.
- Logon Type: The type of login that will take place, when appropriate. The options are:
- Anonymous: You can’t enter a username and password. In this case, the username is always “Anonymous”.
- Normal: You have to enter a username and, if required, a password.
- Ask for password: FileZilla asks you the password during logon, and it remembers the password during the session.
- Interactive: FileZilla asks for the password, and asks again for every new connection to the server.
- Account: Selecting this enables the “Account” field in the bookmark’s settings. This logon type is for FTP only; SFTP does not have support for it.
- Key file: Selecting this enables the use of ssh keys for authentication. This logon type is for SFTP only. You must specify the private key file here, and the server must have your public key.
- User: The user ID to use when connecting.
- Password: Optional.
- Account: Optional.
- Key file: Required when using “Key file” logon type.
- Comments: Optional.
4.2.2 Advanced tab
- Servertype : allows you to make a special selection for this FTP target. Most sites will work fine with the Default value; however, some will require SFTP.
- Bypass proxy: Allows to bypass any proxy server.
- Default local directory field: Allows you to specify a starting local folder when activating a connection. Example: D:\sites\site1
- Default remote directory: Allows you to specify a starting remote sub-folder when activating a connection. Begin it with a / and add only the path that follows the root ftp directory. Example: /public_html
- Time Offset: Allows to adjust the times displayed for files. See the server time offset page for more information.
4.2.3 Transfer Settings tab
Specifies in more detail how transfer may take place.
4.2.4 Charset tab
Specifies the character set used to communicate with the targeted FTP site.
4.3 Using Site Manager
Once you’ve configured your site, select it and click Connect.