How to Scan and Analyze your Wi-Fi?
In RealWiFi. the WiFi Analyzer tool is very easy to use.
- Click “WiFi Analyzer” on the left menu panel to access this tool.
- Click the button “Scan & Analyze”.
- Wait for the scan to complete.
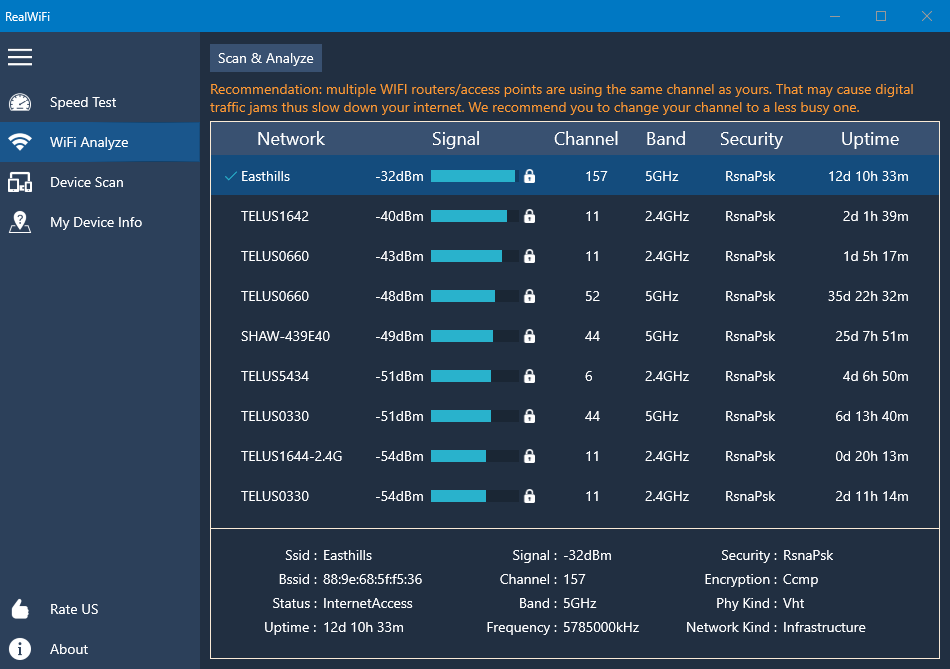
- The tool will automatically provide you recommendations if it find any potential problems. On the other hand, you can always manually analyze the result. The results can be sorted by every column. Click the column header to do the sorting, and click it again to sort the results in the reversed order.
How to Avoid Digital Traffic Jam and Interference?
One main cause of the digital traffic jam is co-channel interference. Co-channel interference is when transmissions occur on the same frequency in the same area. The result is that WiFi is slow or not operable at all. It is a deployment issue that can be resolved with configuration changes.
- In the WiFi Analyzer, sort the scan results by the Channel column and figure out how many networks are using the same channel (frequency) as the connected one.
- If the number is larger than 0, and the other network(s) signal strength, which can be found in the Signal column, is stronger than yours, you should consider changing your channel to a less busy one in your router.
- After changing the channel and rebooting your router, run WiFi Analyzer again to find whether there are any new interferences. If yes, repeat step 2 and 3 until there is no any interferences.
What is dBm, and what constitutes good signal strength?
dBm or dBmW, stands for decibel-milliwatts. Signal strength is measured in dBm, expressed only in negative values.
Here is what the signal strength values mean:
-30 dBm = Excellent – Max achievable signal strength
-67 dBm = Very Good – Minimum signal strength for most business applications
-70 dBm = Okay – Minimum signal strength required for decent packet delivery
-80 dBm = Poor – Minimum signal strength for basic connectivity; Packet delivery may be unreliable.
-90 dBm = Unusable – Any functionality is highly unlikely.